Press Release
At the Solar System’s Edge, More Surprises from NASA’s Voyager
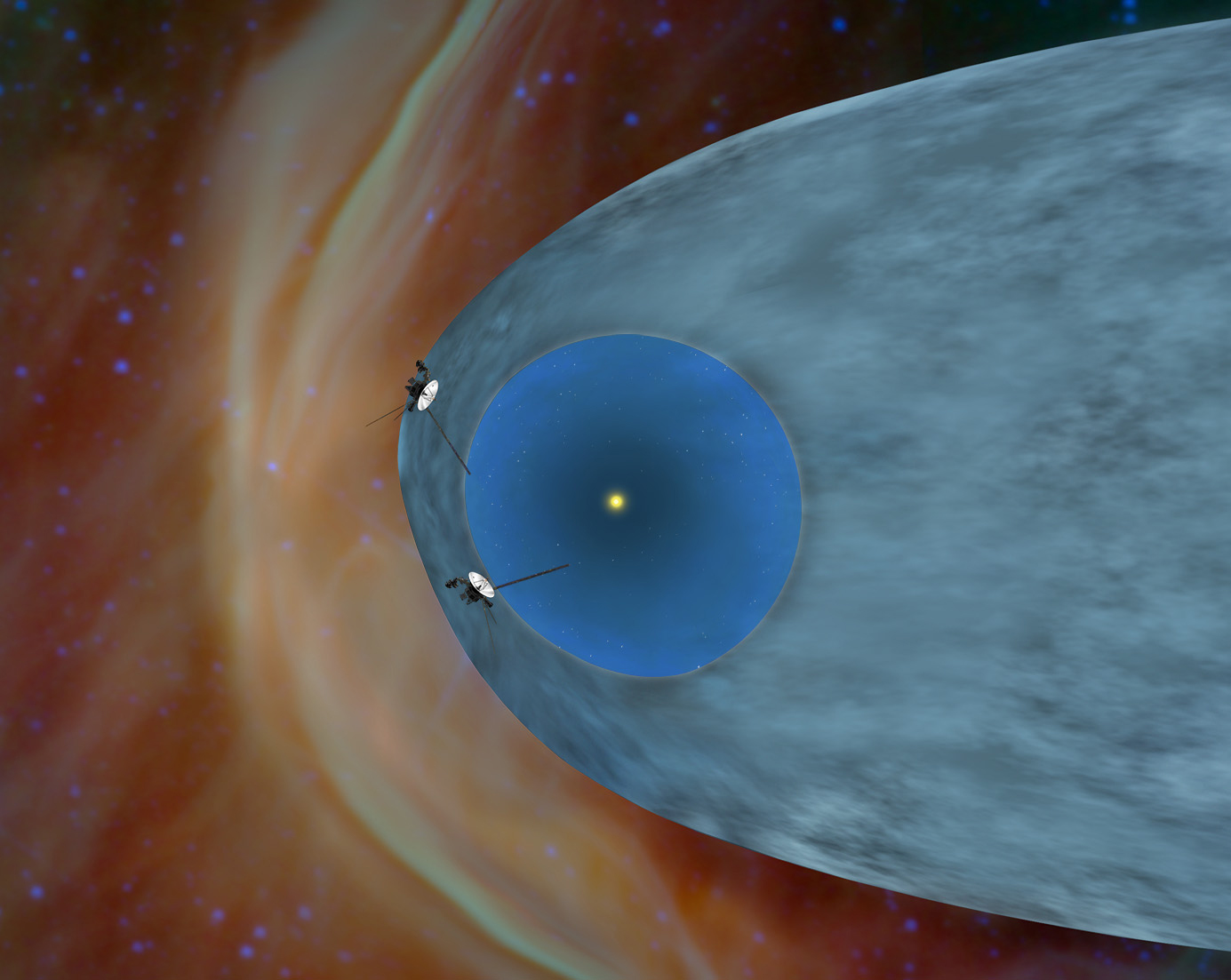
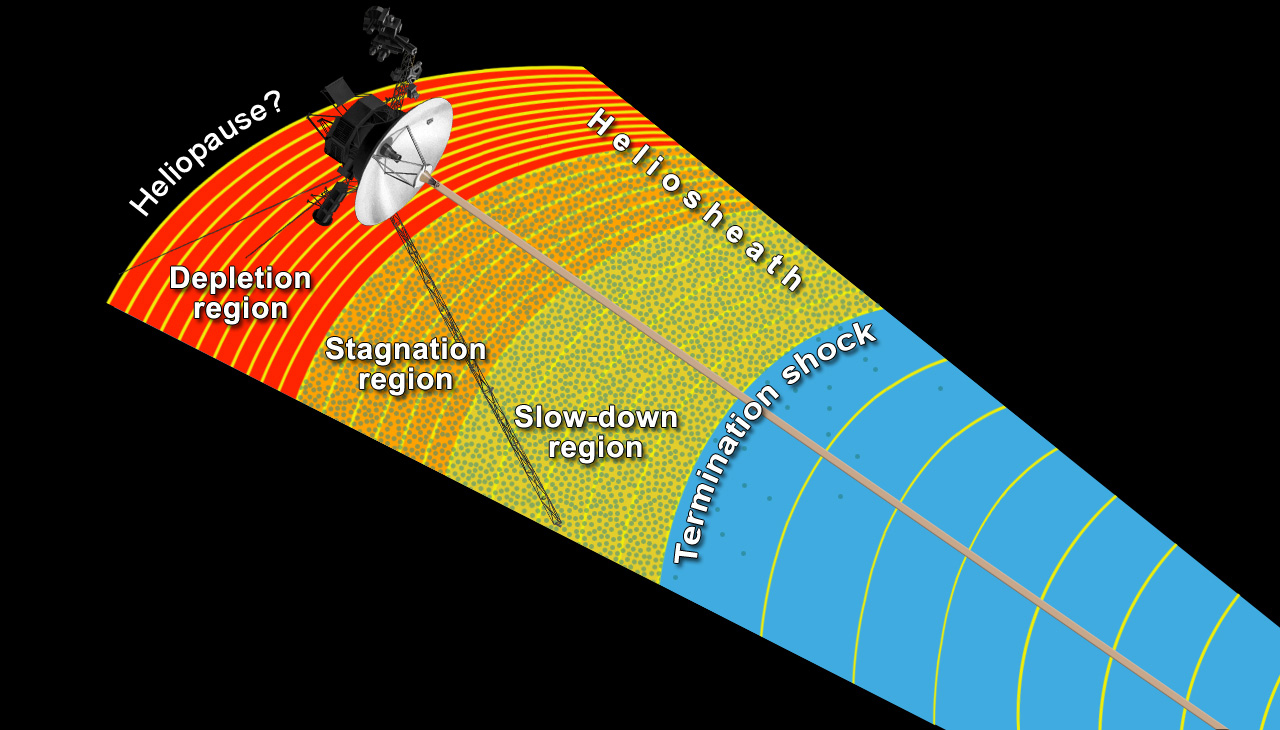
Data from NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft continue to provide new insight on the outskirts of our solar system, a frontier thought to be the last that Voyager will cross before becoming the first man-made object to reach interstellar space.
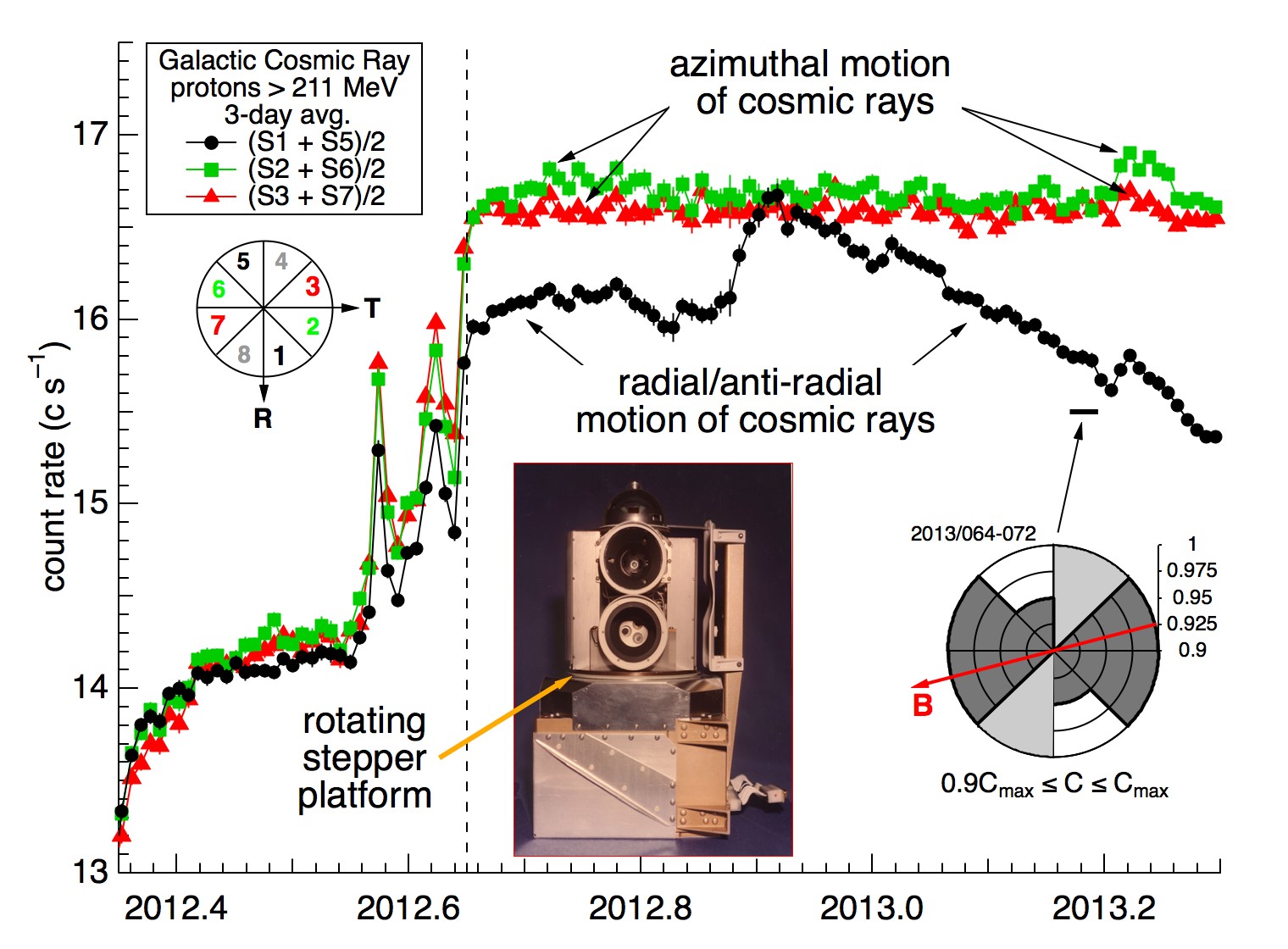
In papers published this week in the journal Science, scientists from the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Md., and other Voyager partner institutions provide more clarity on the region they named the “magnetic highway” in December 2012. Cruising through what scientists describe as a curious, unexpected charged-particle environment, Voyager has detected, for the first time, low-energy galactic cosmic rays, now that particles of the same energy from inside the bubble around our sun disappeared. As a result, Voyager now sees the highest level so far of particles from outside our solar bubble that originate from the death of other nearby stars.
“Voyager 1 may be months or years from leaving the solar system — we just don’t know,” says APL’s Stamatios Krimigis, principal investigator for Voyager’s Low-Energy Charged Particle (LECP) instrument. “But the wait itself is incredibly exciting, since Voyager continues to defy predictions and change the way we think about this mysterious and wonderful gateway region to the galaxy.”